Biotechnology
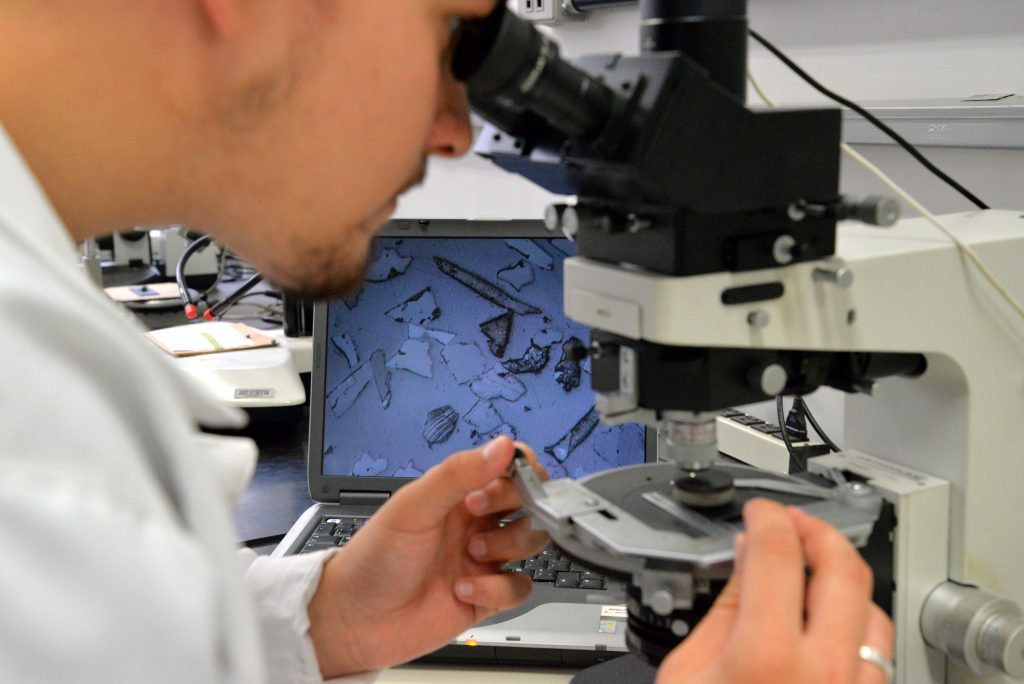
Biotechnology refers to all technological processes involving direct or indirect use of organisms for the production of goods and services pertaining to agriculture, industry, healthcare, and environmental care. The development of biotechnological products and services involves synergic use of technology and basic and applied research. Biotechnology is a cross-cutting, interdisciplinary area essential to the socioeconomic development of any country.
UFMG scholars carry out cutting-edge research on biotechnology in the fields of biological and health sciences, exact sciences, and engineering. This project comprises subprojects related to biotechnology applied to human and animal health.
Agri and Biobusiness
There is potential for expansion and consolidation in the agri and biobusiness sector in Brazil, due to the country's vast territory, climate characteristics and availability of natural resources, in addition to a solid record of basic and applied scientific research hitherto developed in the country. The sector has an important role to play with regard to the world population's food safety. This requires addressing sustainability in the agri and biobusiness development agenda - together with issues such as environmental conservation and mitigation of climate change impacts.
UFMG has an important role in agri and biobusiness improvement by furthering development of state-of-the-art technology in the area and technology transfer to companies. The university conducts research related to this sector in the fields of Animal Science, Food Science and Law. This project aims at innovation and knowledge expansion in animal science; food quality and safety; and regulation in agricultural defense (agrifood law).
Basic sciences and applications.
Basic sciences investigate properties of nature's phenomena. They allow us to understand the world in which we live and foster the development of new technologies to advance exploration and understanding of our universe. Such research is essential for developing theories, experiments and innovative methodologies to analyze complex systems operating at the most diverse temporal and spatial scales.
UFMG carries out cutting-edge research in basic science areas such as Statistics, Physics, Mathematics and their interfaces. This project aims to discuss advanced methodologies for data analysis; star and planet formation and evolution, among other topics.
Big Data and Artificial Intelligence -- New Techniques for Knowledge Extraction, Production, and Use
Several technological advances have enabled the production of large data sets about various aspects of nature and society. Artificial intelligence and big data are investigating how to significantly exploit such data with results significantly impacting a number of daily processes. Systems have been developed to interact with human beings in different contexts and respond to events in unstructured environments.
UFMG scholars carry out cutting-edge research in big data and artificial intelligence at the intersection of the fields of computer science, knowledge management and organization, applied linguistics, political science, and social communication. This project has a twofold aim: 1) to develop new techniques for big data and artificial intelligence with a view to improving usefulness and performance of existing techniques; and 2) to explore the application of big data and artificial intelligence in various human activities.
Industry 4.0
Industry 4.0 is a sustained trend towards developing industrial plants aiming to enhance the integration of components for building complex systems, in turn capable of responding to external demands and internal changes in a fast and flexible manner. While the third industrial revolution was concerned with automation and data acquisition, Industry 4.0 is concerned with connectivity, real time processes, and use of data for autonomous, optimized decision making.
This project focuses on digitization, sensorization, and optimization. Its goal is to develop new technologies, reduce costs, improve quality, increase production efficiency and maximize the financial return and social benefit of modern production processes.
Languages in Digital Contexts
Language varieties and variation is a complex theme and a major contemporary challenge. In the 21st century, human language has evolved new forms and new uses, responding to changes in its production, consumption, and communication.
This project aims to study how the various forms of language operate and evolve in an increasingly connected world by mapping the use of oral and written language in digital contexts as well as computer tools for human-machine interfaces for production and translation of technical and colloquial texts.
Creative Educational Solutions
Education has become a global concern due to constant and increasingly faster social changes, as well as new actors and processes. Educational and cultural policies have been included in the agenda of major debates since the beginning of the 20th century with a view to strengthening solidarity and peace, controlling the growing rise of radical ideologies, and eradicate violence.
Education is an important issue in contemporary societies because of its potential to promote conflict avoidance and create alternative pathways to challenge the globalization of capital, the revolution of mass media and communication techniques, and the advent of new technologies and their massive impact on people as factors aggravating the existing social inequality both between individuals and between nations. This project approaches topics such as educating for sustainability; developing social and educational technology targeting children, young people, and institutions; and training healthcare educators and researchers for the 21st century.
New Materials and Nanotechnology
New technologies -- from the stone age to the age of molecular biology – have always drawn on the development of new materials, as energy production and storage, information processing, machinery and biomedical solutions, among others, are based properties of those materials. The limited supply of minerals and the threat of global warming call for the development of new materials for enhanced energy efficiency and lower environmental impact. Nanotechnology is the most advanced stage in materials science, dealing with matter at the molecular level to enable control of processes on a large scale or to develop large quantities of superior materials.
UFMG scholars carry out cutting-edge research in new materials and nanotechnology at the intersection of computer science, pharmaceutical sciences, engineering, physics, dentistry, and chemistry. This project comprises subprojects targeting nanocomputing and computational nanotechnology, and development of materials with advanced properties for biomedical applications.
Cities and Territories
Every city, regardless of its size, has the potential to develop its own cultural activities and creative industries, sustainable standards, smart structures and connectivity networks, as well as well-being and principles of gender equality, social values and political traditions. Over half of the world population dwells in urban areas, who also account for approximately 60% of the world's GDP.
UFMG scholars carry out benchmark research on cities and territories at the intersection of architecture and urbanism, computer science, law, economics, leisure studies, history, geography, dentistry, and public health. This project comprises subprojects targeting contemporary debates on urbanization, territory, nature and development; as well as sports and leisure policies.